
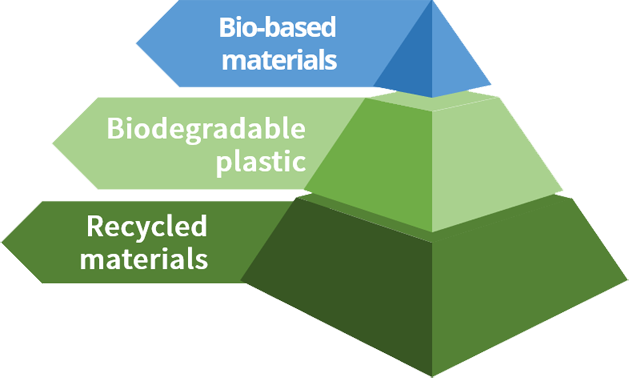

The difference between bio-based materials and traditional materials is that part or all of the ingredients use renewable biomass such as grains, legumes, straw, bamboo and wood powder as raw materials, which are converted into chemical monomers and further polymerized into polymer materials.
Compare with traditional polymer materials, bio-based materials have two advantages:
With the growing development of bio-based materials, the types and specifications of bio-based materials are also more diversified; Nytex has long been committed to the research and development of various bio-based materials in the field of engineering plastics, recommending materials for customers' applications, not only helping customers reduce the carbon footprint of end products, and at the same time contribute to the sustainable management of the environment.
Biodegradable plastics, also known as green plastics, are characterized in that they can be metabolized and decomposed by microorganisms in the environment under certain environmental conditions (sufficient humidity, oxygen and appropriate microorganisms), and the decomposed products (ie water, carbon dioxide , methane, etc.) make the harm to the environment much less.
Nytex has long regarded environmental protection as its own responsibility, and it is also the focus of development that Nytex pays attention to. Nytex combines the existing composite material technology with the characteristics of biodegradable plastics to develop biodegradable modified materials with good dyeability, easy processability and disposable decomposition, which are widely used in household products, outdoor products, structural housing materials.
In addition, Nytex also noticed that as survival games become more and more popular, the use of BB bullets is also increasing day by day. These BB bullets scattered on the soil will not disappear by themselves, but will seep into the soil with rainwater, poison the land, be absorbed by plants, and eventually return to human bodies along the food chain. In order to improve this situation, Nytex started to develop and launched a new product "Biodegradable polymer material for BB bullets", so that enjoying survival games no longer has to be equated with causing pollution to the environment.

With the increasing use of plastic products, the output of plastic waste is also increasing day by day; for such materials that are difficult to decompose naturally, artificial treatment and recycling have gradually become a trend. GRS certification is one of the certifications for recycled materials.

GRS certification, full name Global Recycled Standard, is an international general and voluntary product specification requirement standard; to obtain GRS certification, products must contain at least 20% certified recycled materials and be 100% pollution-free. In addition to the source of raw materials, GRS also regulates the corporate social responsibility, the control of environmental pollution during the production process, and the use of toxic chemicals.
Nytex has long been committed to the development of composite projects of recycled materials, and regards the physical and mental health of employees and the sustainable development of the environment as the first priority; therefore, Nytex has started applying at the end of 2021, and obtained the GRS certification in early 2022.

| Grade GT-0010N HT | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Test Items | Result | Conclusion | Test Report No. | ||
| Material Analysis | Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR) | Main constituent: PLA | CY/2013/40618 | ||
| Heat-Resistance | 140°C | Appearance not changed | CY/2013/40619 | ||
| Cold-Resistance | -20°C | No crack | CY/2013/41358 | ||
| Potassium permanganate consumption | Migration test: (water, 60°C, 30min) | Not Detected | The test results comply with the limits of requirements in Article 6 of Sanitation Standard for Food Utensils, Containers and Packages (DOH Food No. 1021300776 was amended on 2013/04/09). | CY/2013/40617 | |
| Heavy metal (Pb) | Migration test: (4% acetic acid, 60°C, 30min) | Undetectable | |||
| Total lactic acid | Migration test: (water, 60°C, 30min) | Not Detected | |||
| Evaporation residue | Migration test: (water, 60°C, 30min) | Not Detected | |||
| Migration test: (4% acetic acid, 60°C, 30min) | Not Detected | ||||
| Migration test: (20% alcohol, 60°C, 30min) | Not Detected | ||||
| Melamine | Migration test: (4% acetic acid, 95°C, 30min) | Not Detected | CY/2-13/40616 | ||
| Bi s phenol A | Migration test: (4% acetic acid, 60°C, 30min) | Not Detected | |||
| Plasticizer (1) | EDHP | Migration test: (n-Heptane, 25°C, 1 hour) | Not Detected | The test results comply with the limits of requirements in Article 6 of Sanitation Standard for Food Utensils, Containers and Packages (DOH Food No. 1021300776 was amended on 2013/04/09). | CY/2013/40615 |
| DBP | Not Detected | ||||
| DINP | Not Detected | ||||
| DIDP | Not Detected | ||||
| BBP | Not Detected | ||||
| DEHA | Not Detected | ||||
| DNP | Not Detected | ||||
| Plasticizer (2) | DEHP | With reference to CNS 15138 method. Analysis was performed by GC/MS. | Not Detected | CY/2013/40614 | |
| DBP | Not Detected | ||||
| BBP | Not Detected | ||||
| DIDP | Not Detected | ||||
| DINP | Not Detected | ||||
| DMP | Not Detected | ||||
| DNOP | Not Detected | ||||
| DEP | Not Detected | ||||
| Pb | With reference to Sanitation Standard for Food Utensils, Containers and Packages-Plastics (DOH Food No. 1001902289 Amended and Appended, July 2011). Analysis was performance by ICP-AES. | Not Detected | The test results comply with the limits of requirements in Article 6 of Sanitation Standard for Food Utensils, Containers and Packages (DOH Food No. 1021300776 was amended on 2013/04/09). | CY/2013/40613A | |
| Cd | Not Detected | ||||
| Cu | ICP-AES after as per acid digestion. | Not Detected | |||
| Hg | Not Detected | ||||
| Ni | Not Detected | ||||
| Cr | Not Detected | ||||
